In rats or mice bearing a unilateral 6-OHDA-induced lesion of the nigrostriatal tract, repeated administration of L-DOPA induces a dyskinesia-like phenotype, abnormal involuntary movement (AIMs). The potential of treatments to reduce established AIMs or to impact on the development of AIMs when given de novo can be effectively assessed in this well-validated model.
- Well characterised rodent model of Parkinson’s disease
- Rapid evaluation of test compounds
- Ideal for mechanistic studies with post-mortem endpoints
Model Overview
Rats or mice, previously made hemi-parkinsonian with 6-OHDA are administered L-DOPA (10-15 mg/kg, q.d.) for a period of 2-3 weeks until the development of AIMs. Once established, dyskinesia is robust and stable upon repeat L-DOPA challenge and can be maintained over several months allowing test compounds to be thoroughly evaluated in the same cohort of animals. Alternatively, compounds can be administered alongside L-DOPA using a parallel group design to assess effects on the development of AIMs.
AIMs can be reversed by pharmacological intervention
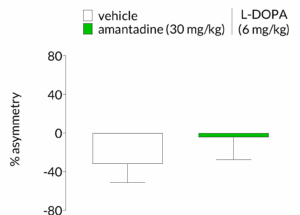
L-DOPA-induced AIMs can be reduced by a wide range of pharmacological interventions. In this example, amantadine, an NMDA receptor antagonist, significantly reduces established L-DOPA induced AIMs.

Effect of test compounds on dyskinesia and parkinsonian symptoms can be assessed in the same animals
It is critical that compounds that reduce L-DOPA induced dyskinesia do so without reducing the antiparkinsonian benefits of L-DOPA. A test of forelimb asymmetry such as the cylinder test can evaluate the effect of a test compound on L-DOPA actions and provide crucial support for continued development.
Available in-vivo imaging
Assessments of target-engagement can be readily made using micro-PET or micro-SPECT. On-site radiochemical and cyclotron facilities provide support for production of common and speciality ligands.

Experimental readouts
- Behavioural – Behavioural endpoints include the rodent AIMs scale and automated rotometry alongside crucial tests of forelimb asymmetry (cylinder and stepping tests) to ensure any effect of treatments to reduce AIMs does not impact on the anti-parkinsonian benefit of L-DOPA. Additional behavioural endpoints can include rotarod, beam-balance and staircase tests.
- Pharmacokinetics, safety and blood chemistry – Pharmacokinetics and associated bioanalysis can be incorporated into all studies. Blood can be sampled throughout the study and brain and CSF samples can be terminally collected .
- Post-mortem – Rodent AIMs models are perfect for comprehensive post-mortem analyses. Typical markers can include assessment of pre-proenkephalin A and B levels via in-situ hybridisation, DARPP32 via Western Blotting, neurotransmitter receptor-binding assays. Additional post-mortem measures can be incorporated at the client’s request.
- Imaging – We offer both micro-PET / SPECT imaging that allows for target-engagement studies and for longitudinal measurement of markers of brain metabolism (e.g. FDG PET).