Systemic administration of MPTP to non-human primates produces abehavioural phenotype that recapitulates the motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. MPTP induces a robust and stable parkinsonian syndrome that includes bradykinesia and postural impairment. The model is highly predictive of potential Phase II efficacy in alleviating parkinsonism or enhancing the effects of dopaminergic therapies.
- Well characterised primate model of Parkinson’s disease
- Behavioural endpoints similar to endpoints used in clinical studies
- Exceptional translatability for assessing symptomatic therapies
Model Overview
MPTP (0.2 mg/kg, i.v.) is administered to cynomolgus macaques over a period of several weeks and titrated to produce the required severity of parkinsonian phenotype. The degree of parkinsonism is stable and persists over many years allowing both the acute and chronic effect of compounds to be evaluated.
Dopamine agonists reverse MPTP-induced parkinsonism
Parkinsonian symptoms induced by MPTP is reversed by compounds, such as ropinirole (shown), which, along with L-DOPA form the mainstay of symptomatic treatment for patients with Parkinson’s disease.

| Compound class | NHP | Phase II |
|---|---|---|
| ropinrole | Yes ✅ | Yes ✅ |
| pramipexole | Yes ✅ | Yes ✅ |
| sumanirole | Yes ✅ | Yes ✅ |
| preladenant | Yes ✅ | Yes ✅ |
| istradefylline | Yes ✅ | Yes ✅ |
| vipadenant | Yes ✅ | Yes ✅ |
| tozadenant | Yes ✅ | Yes ✅ |
| entacapone | Yes ✅ | Yes ✅ |
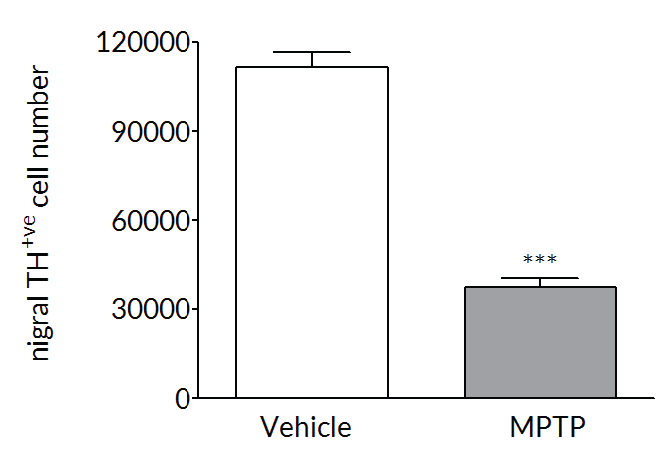
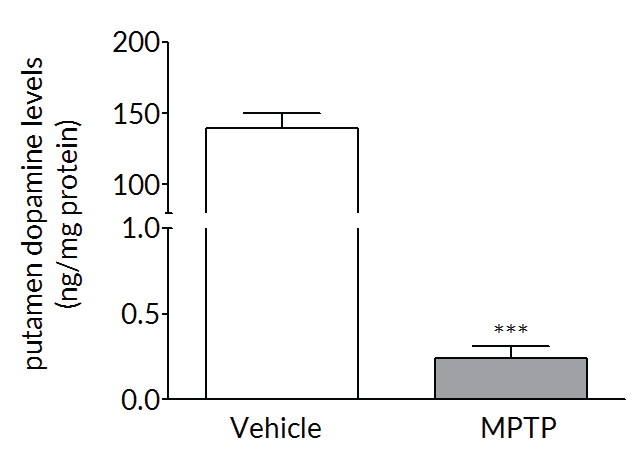
MPTP produces a robust dopaminergic lesion
Repeated MPTP administration causes a loss of tyrosine hydroxylase positive neurons in the substantia nigra (left) and a loss of dopamine in the striatum (right) – both classic hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease.
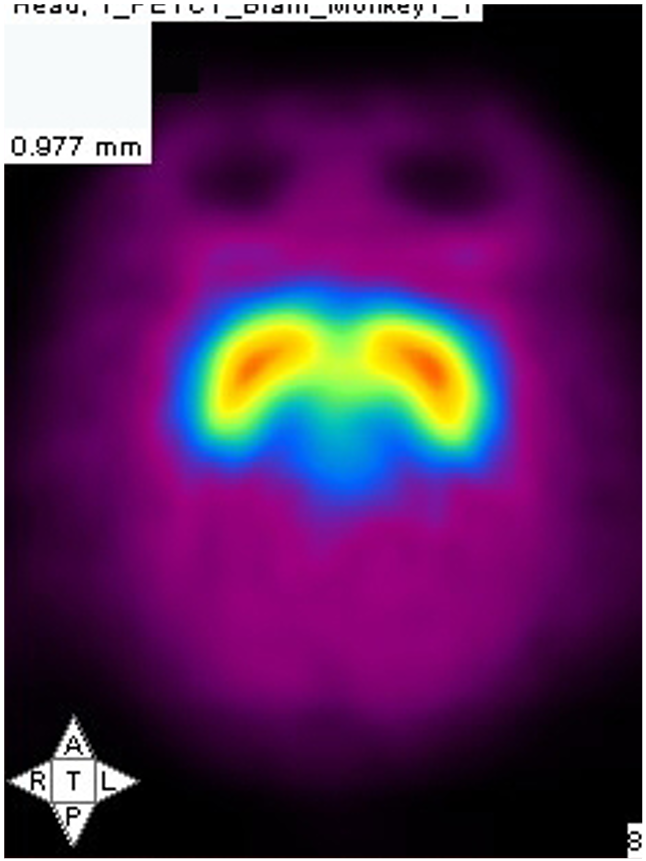
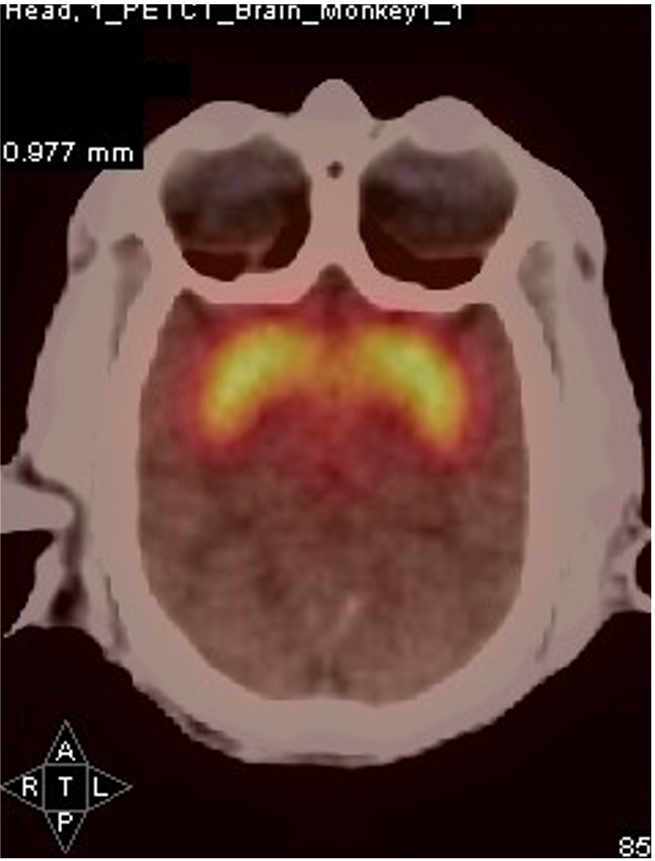
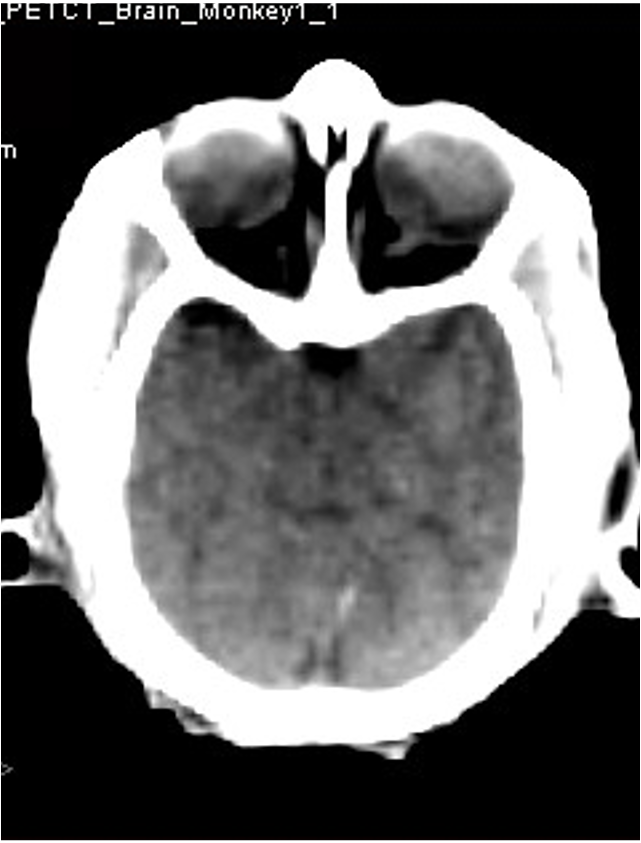
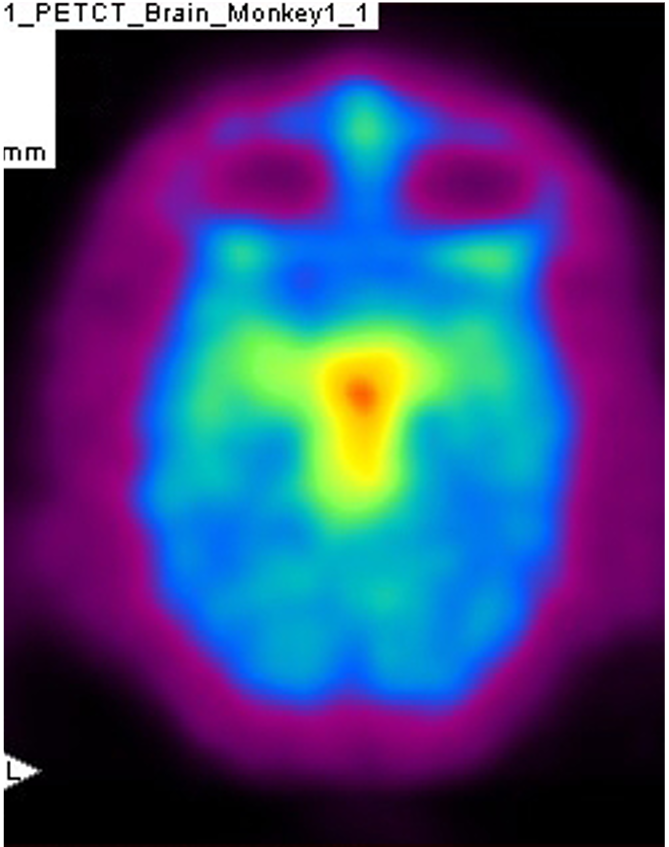
PET imaging allows in-life assessment of dopaminergic cell loss
Striatal levels of markers of the dopaminergic system (VMAT and DAT) can be imaged throughout longitudinal studies – allows the effect of compounds to be followed over time.
Control
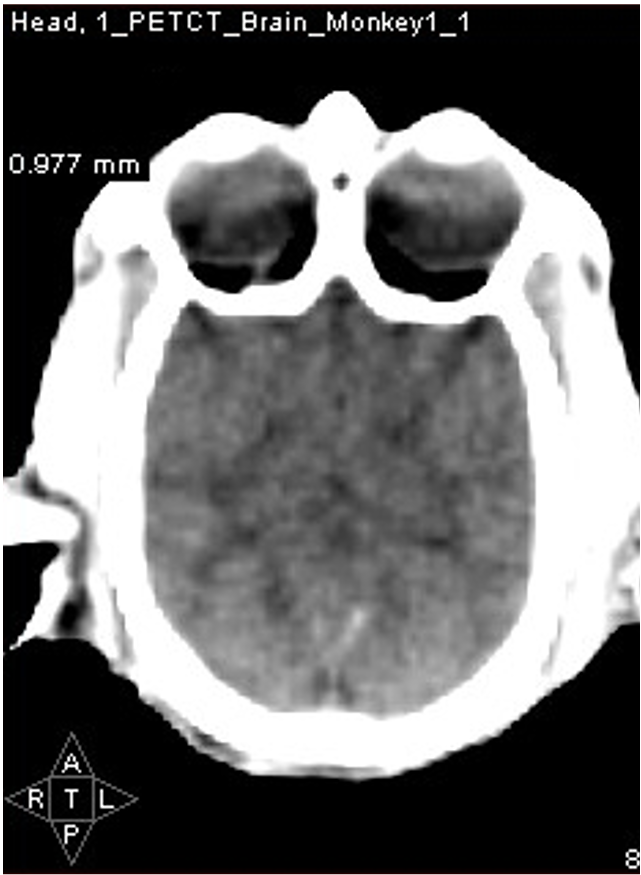
MPTP
Experimental readouts
- Behavioural – Behavioural assessments include the monkey parkinsonian disability rating scale, the monkey equivalent of the clinical rating scales used to assess disability in people with Parkinson’s disease. Additional behavioural endpoints include home-cage activity, observation-cage activity and fine motor control.
- Post-mortem – Routine post-mortem analyses include striatal dopamine and dopamine transporter (DAT) and the number of number of tyrosine-hydroxylase positive cells in the substantia nigra. Additional post-mortem measures can be incorporated at the request of the client.
- Pharmacokinetics, safety and blood chemistry – Can be incorporated into all studies. Blood and CSF can be sampled throughout the study and terminal samples of brain and other tissues can be collected. Functional observational battery and blood chemistry can be used to assess off-target and adverse effects.
- Imaging – We offer both MRI and PET imaging that allows longitudinal measurement of markers of dopaminergic function and metabolism.